Unraveling Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comprehensive Guide - Dr Markandaiya Acharya
Introduction
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate world of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Our mission is to provide you with a thorough understanding of RA, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies. By the end of this article, you'll be equipped with valuable insights into this condition, helping you make informed decisions regarding your health.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Rheumatoid Arthritis, often abbreviated as RA, is a complex autoimmune disease. Unlike osteoarthritis, which primarily affects the joints due to wear and tear, RA involves the immune system mistakenly attacking the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. This leads to inflammation, pain, and eventual joint damage. RA typically affects multiple joints simultaneously, and it can also impact other organs, making it a systemic condition.
Key Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
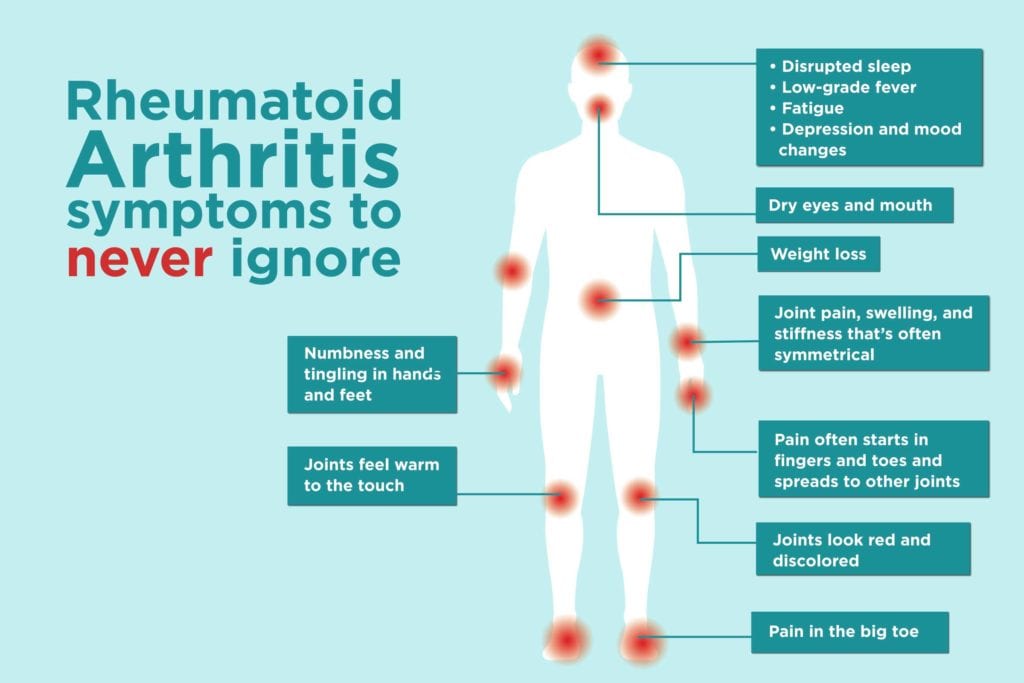
Recognizing the symptoms of RA is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Here are some common signs to look out for:
1. Joint Pain and Stiffness
RA often starts with mild joint pain and stiffness, which can progress to severe discomfort. Morning stiffness that lasts for more than an hour is a hallmark symptom.
2. Swelling and Inflammation
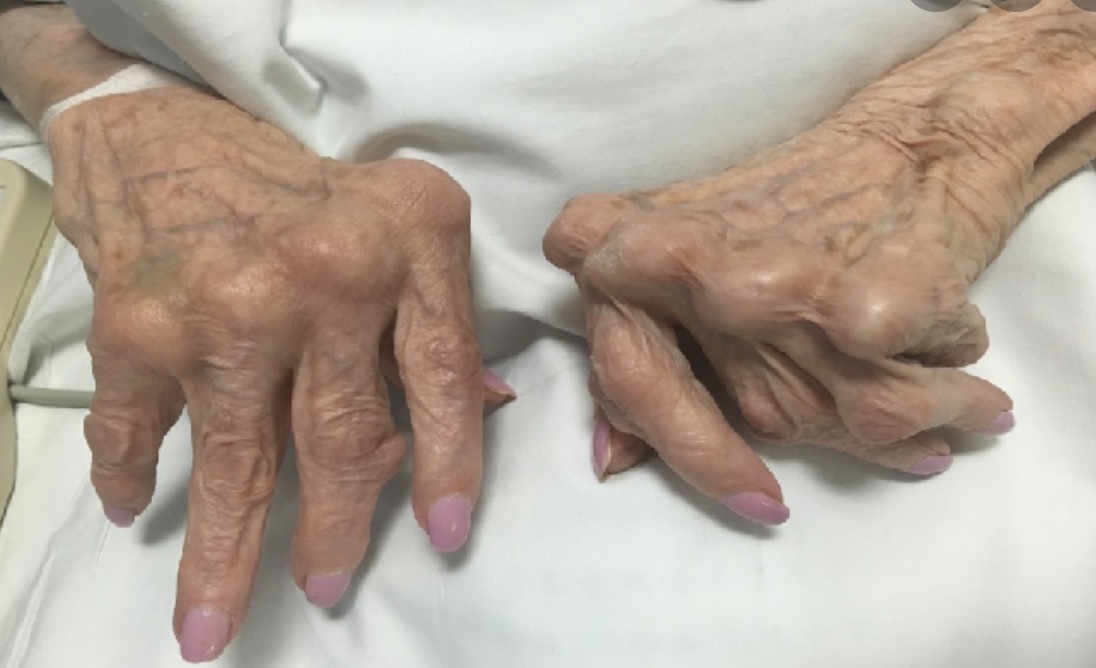
Inflamed joints may appear swollen and feel warm to the touch. This inflammation can cause joint deformities over time.
3. Fatigue
Many RA patients experience persistent fatigue, often unrelated to physical activity, which can significantly impact daily life.
4. Joint Deformities
If left untreated, RA can lead to joint deformities, affecting your ability to perform routine tasks.
5. Fever and Weight Loss
In some cases, RA may cause fever and unintentional weight loss, indicating systemic involvement.
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Accurate diagnosis is essential to initiate timely treatment. To diagnose RA, healthcare providers typically consider several factors:
1. Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination helps identify swollen, tender joints and other symptoms.
2. Blood Tests
Blood tests, such as the Rheumatoid Factor (RF) and Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (anti-CCP) antibody tests, can detect specific markers associated with RA.
3. Imaging
X-rays, ultrasounds, and MRI scans may be used to assess joint damage and inflammation.
Treatment Options
RA management aims to control inflammation, alleviate pain, and prevent joint damage. Treatment options include:
1. Medications
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) to slow disease progression.
- Biologics that target specific components of the immune system.
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can improve joint function and reduce pain.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Dietary adjustments and regular exercise can complement medical treatment.
Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with RA requires proactive self-care. Here are some strategies to manage the condition effectively:
1. Medication Adherence
Follow your prescribed medication regimen diligently.
2. Joint Protection
Use assistive devices and ergonomic techniques to protect your joints.
3. Regular Check-ups
Visit your rheumatologist regularly for monitoring and adjustments to your treatment plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Rheumatoid Arthritis is a complex autoimmune disease that can significantly impact your quality of life. Early diagnosis and comprehensive management are crucial for better outcomes. We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into RA, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health. If you suspect you have RA or have recently been diagnosed, consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment options. Your journey towards better health begins with knowledge and proactive care.



Comments
Post a Comment