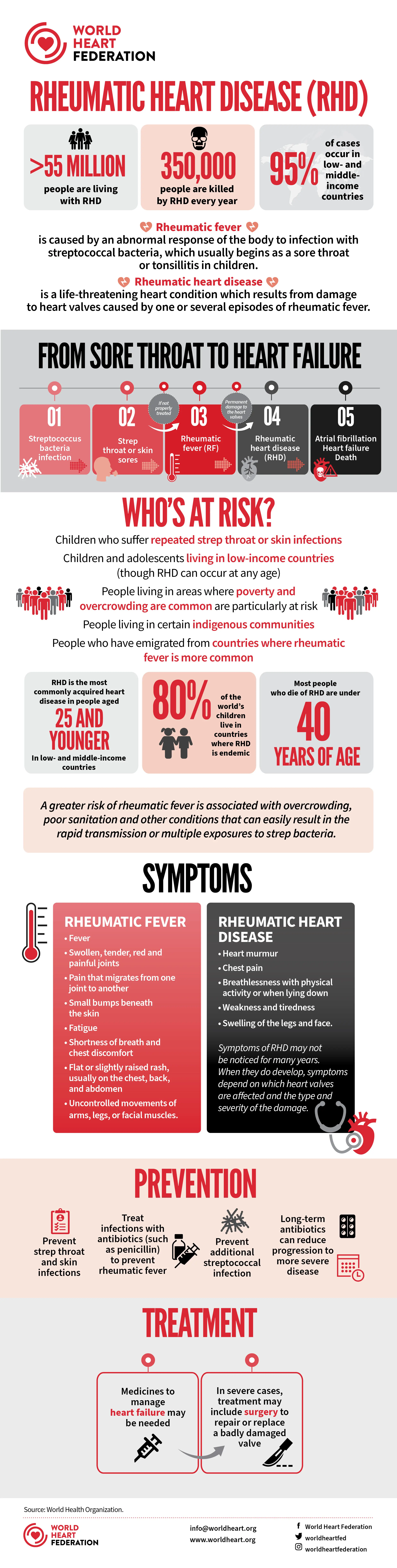
Rheumatic Heart Disease (RHD): A Serious Public Health Challenge
Imagine a world where a sore throat, a seemingly trivial inconvenience, could lead to a life-threatening heart condition. This isn't a distant dystopia, but the harsh reality for millions living in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) facing a silent, insidious threat: rheumatic heart disease (RHD).
(Source: World Heart Federation)
A Devastating Ripple Effect: From Strep Throat to Heart Damage
RHD is a crippling condition that damages the heart valves due to untreated rheumatic fever, a complication arising from a seemingly ordinary strep throat infection. In high-income countries, antibiotics make strep throat a manageable issue. However, in LMICs, limited access to healthcare creates a breeding ground for this seemingly minor infection to snowball into a major heart problem.
The consequences of untreated rheumatic fever are severe. The inflamed tissues in the throat can attack the heart valves, causing scarring and narrowing. This disrupts the smooth flow of blood, eventually leading to heart failure, irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), and even stroke.
A Grim Reality: High Mortality and Lack of Access to Treatment
A recent large-scale study involving patients from 24 LMICs paints a concerning picture. The study revealed a staggeringly high mortality rate: nearly 15% of participants with RHD died within a mere three years. Heart failure and sudden cardiac death were the leading causes of death, highlighting the severity of this neglected disease.
Even more alarming is the fact that despite experiencing symptoms, only about 5% of participants received corrective valve surgery or valvuloplasty during the study period. Valve surgery repairs or replaces damaged valves, while valvuloplasty opens narrowed valves. These procedures are life-saving interventions, and their underutilization suggests a critical gap in access to essential cardiac care within LMICs.
A Beacon of Hope: Surgical Interventions Offer a Lifeline
However, the study also offers a glimmer of hope. It found that patients who underwent valve surgery or valvuloplasty had a significantly reduced risk of death compared to those who didn't. This finding underscores the critical role these procedures play in improving outcomes for RHD patients. Expanding access to these life-saving treatments in LMICs is an urgent necessity.
Identifying the Vulnerable: Early Diagnosis and Risk Factors
The study also shed light on factors that increase the risk of death in RHD patients. Markers of severe valve disease, such as congestive heart failure, where the heart struggles to pump blood efficiently, pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the lungs), and atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat in the upper chambers of the heart), were all linked to higher mortality rates.
This emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and management of RHD. By identifying the disease early and intervening before complications arise, we can dramatically improve patient outcomes and prevent needless deaths. Early diagnosis often involves listening for abnormal heart sounds with a stethoscope and using echocardiograms, which are ultrasound images of the heart, to assess valve function.
The Socioeconomic Disparity: Poverty as a Risk Factor
Interestingly, the study revealed a correlation between socioeconomic status and mortality rates. Patients from wealthier LMICs had a lower mortality risk compared to those from poorer countries. This suggests that poverty itself is a risk factor for RHD patients. Limited access to healthcare infrastructure, qualified medical professionals, and advanced diagnostic tools in poorer nations likely contribute to this disparity.
A Multi-Faceted Approach: Fighting RHD on All Fronts
Winning the fight against RHD requires a multi-pronged approach. Expanding access to surgical and interventional procedures like valve surgery and valvuloplasty is crucial to saving lives. Continued efforts in preventing strep throat with antibiotics and preventing blood clots with medication like anticoagulants are also essential in preventing the initial trigger and subsequent complications of RHD.
Beyond Treatment: Addressing the Root Cause: Poverty and Healthcare Inequality
However, the most critical step lies in addressing the root cause: poverty and unequal access to healthcare. By strengthening healthcare systems in LMICs, we can ensure that everyone, regardless of their income or location, has access to quality preventive care, early diagnosis, and essential treatments for RHD.
This includes investing in infrastructure to build well-equipped healthcare facilities, training more doctors and nurses specializing in heart health, and implementing affordable healthcare programs to reduce the financial burden on patients.
Investing in the Future: Education and Community Awareness
Education and community awareness play a vital role in the fight against RHD. Educating people about the importance of good hygiene to prevent strep throat infections and the early signs and symptoms of RHD can empower communities to seek timely medical attention. Additionally, advocating for policies that prioritize affordable healthcare accessibility in LMICs is crucial for long-term progress.
Preventable Tragedy: Breaking the Cycle of RHD
Rheumatic heart disease is a preventable tragedy. By focusing on both prevention and treatment strategies, we can break the cycle of this devastating disease and offer a brighter future for millions living in LMICs.
Here are some key steps we can take:
Strengthening Primary Healthcare Systems: Investing in primary healthcare infrastructure in LMICs is crucial. This includes building well-equipped clinics, training more healthcare workers, and establishing robust referral systems for patients requiring specialized cardiac care.
Promoting Early Diagnosis and Management: Educational programs for healthcare workers in LMICs can enhance their ability to diagnose RHD early using stethoscopes and echocardiograms. Early detection allows for prompt intervention with antibiotics to treat active rheumatic fever and medications to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Scaling Up Access to Antibiotics: Ensuring widespread availability and affordability of antibiotics in LMICs is essential. This can be achieved through initiatives that promote responsible antibiotic use, negotiate lower drug prices, and establish local production facilities.
Investing in Research and Development: Continued research is vital to develop new, more affordable diagnostic tools, refine surgical techniques, and explore alternative treatment options for RHD patients in resource-limited settings. Additionally, research into novel vaccines or preventative measures for strep throat could hold immense promise in the long run.
Collaboration is Key: A United Front Against RHD
Combating RHD effectively requires collaboration on various fronts. International organizations, national governments, healthcare institutions, and NGOs all have vital roles to play.
International Organizations: Global health organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) can provide crucial leadership by developing evidence-based guidelines for RHD prevention and treatment, advocating for increased funding for LMIC healthcare systems, and fostering international collaboration on research and development.
National Governments: Governments in LMICs have a responsibility to prioritize strengthening their healthcare systems, promoting affordable access to antibiotics and essential cardiac medications, and investing in educating healthcare workers about RHD diagnosis and management.
Healthcare Institutions: Hospitals and clinics in LMICs can play a key role by establishing dedicated RHD clinics, training their staff in RHD care, and advocating for improved access to diagnostic tools and treatment options.
NGOs: Non-governmental organizations can contribute significantly by raising awareness of RHD, supporting community-based educational programs, and mobilizing resources to support RHD prevention and treatment initiatives in LMICs.
Empowering Individuals and Communities: Taking Charge of Heart Health
Individuals and communities in LMICs also have a role to play in combating RHD. Here's how:
Promoting Good Hygiene: Educating communities about the importance of good hygiene practices like handwashing can significantly reduce the spread of strep throat infections, a crucial step in preventing RHD.
Seeking Early Medical Attention: Raising awareness about the signs and symptoms of RHD can empower individuals to seek timely medical attention if they experience symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, or chest pain.
Advocacy: By advocating for policies promoting affordable healthcare access and RHD prevention programs, individuals and communities can contribute to systemic change and ensure better long-term outcomes.
Conclusion: A Brighter Future for All
Rheumatic heart disease is a serious yet preventable public health challenge with a devastating impact on millions in LMICs. By prioritizing access to quality healthcare, promoting early diagnosis and treatment, and investing in research and education, we can break the cycle of RHD. Through collaborative efforts between international organizations, national governments, healthcare institutions, NGOs, and individuals, we can create a brighter future where everyone, regardless of their income or location, has the opportunity for a healthy heart and a fulfilling life.


Comments
Post a Comment