All about Rheumatoid Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased mobility. While there is no cure for RA, effective management strategies can help individuals live fulfilling lives.
Image: Rheumatoid Hand
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
RA is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body's immune
system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues. In the case of RA, the immune system
targets the synovium, the tissue that lines the joints. This inflammation can
lead to joint damage, erosion, and deformity.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of RA remains elusive, it is widely
believed to be a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors.
Understanding these risk factors can help shed light on the disease and inform
prevention and treatment strategies.
Image: Causes and Risk Factors of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Genetic Predisposition
A family history of RA or other
autoimmune diseases can significantly increase an individual's risk of
developing the condition. This suggests that genetic factors play a crucial
role in determining susceptibility. Researchers are actively investigating specific
genes that may be involved in RA, with the hope of identifying individuals at
high risk and developing targeted therapies.
Age and Gender
RA typically develops in
adulthood, with the peak onset occurring between the ages of 40 and 60.
However, it is important to note that younger individuals can also be affected.
Additionally, women are more likely to develop RA than men, although the reasons
for this gender disparity are not fully understood. Hormonal factors may play a
role, as evidenced by the fluctuations in RA symptoms during pregnancy and
menopause.
The Impact of Smoking
Smoking is a well-established
risk factor for RA. Studies have consistently shown that individuals who smoke
are more likely to develop the disease and experience more severe symptoms.
Smoking can also accelerate the progression of RA, leading to joint damage and
disability. Quitting smoking is crucial for individuals with RA or those at
risk of developing the condition.
Hormonal Influences
Hormonal changes can influence
the development and progression of RA. For example, pregnancy and menopause are
associated with fluctuations in RA symptoms. These hormonal shifts may affect
the immune system's activity and contribute to the development of the disease.
Further research is needed to fully understand the role of hormones in RA and
to explore potential therapeutic interventions.
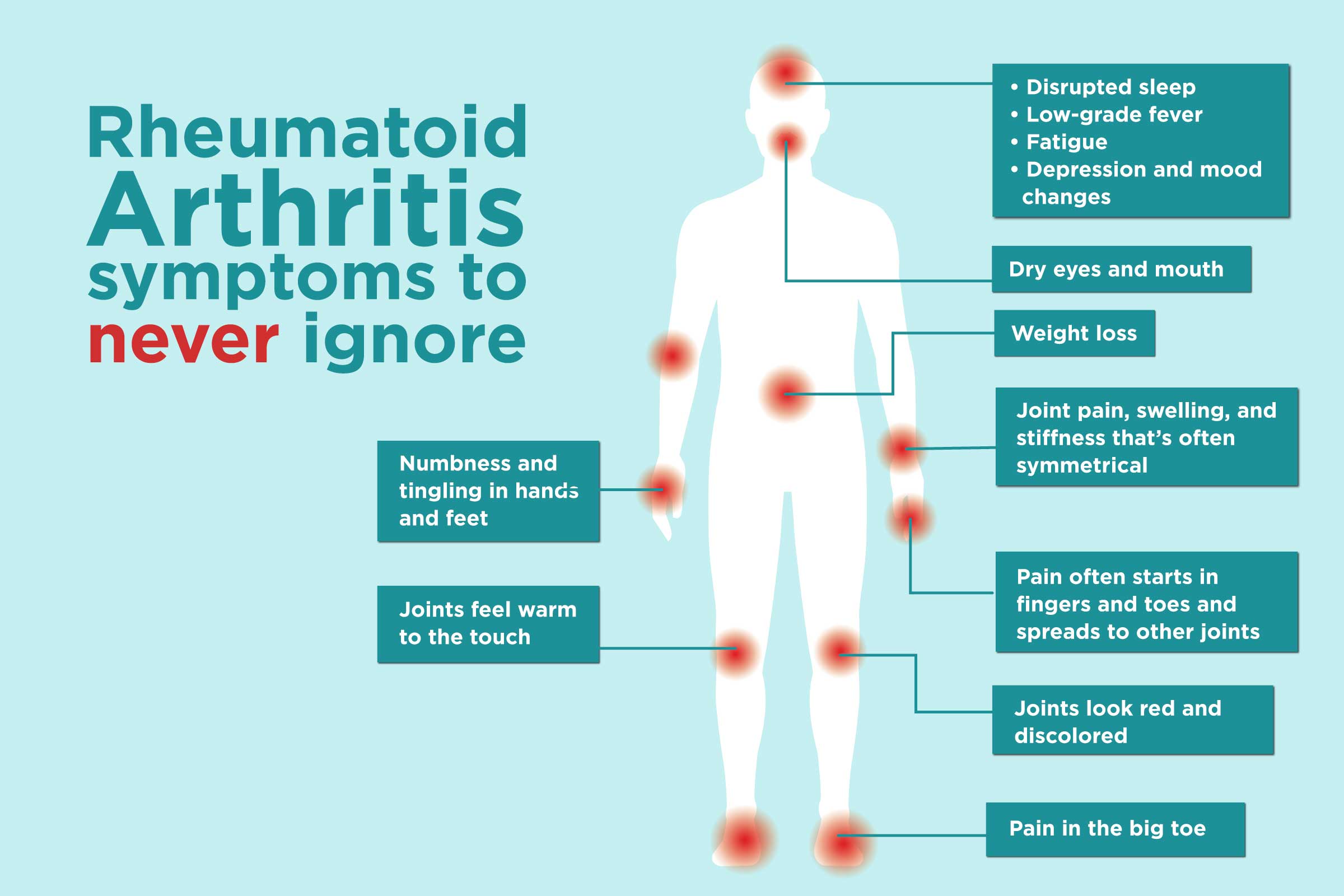
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
It can manifest in a variety of ways. While the symptoms of
RA can vary from person to person and may change over time, certain common
patterns emerge.
Image: Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Joint Pain and Tenderness
One of the most prominent
symptoms of RA is joint pain and tenderness. These sensations often occur in
the hands, wrists, feet, and ankles, but can also affect other joints in the
body. The pain may be described as a dull ache, a sharp stabbing pain, or a
burning sensation.
Swelling and Redness
Inflammation is a hallmark of RA.
This inflammation can lead to swelling and redness in the affected joints. The
swelling may be accompanied by warmth and tenderness to the touch.
Morning Stiffness
A common symptom of RA is
stiffness, particularly in the morning. This stiffness can make it difficult to
move the joints upon waking and may last for several hours.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a common symptom of RA
and can significantly impact a person's quality of life. This fatigue is often
unrelated to physical activity and can be accompanied by a general feeling of
malaise.
Weight Loss
Unintended weight loss is another
potential symptom of RA. This weight loss can be due to a number of factors,
including decreased appetite, increased energy expenditure, and inflammation.
Fever
In some cases, RA can be
associated with a low-grade fever. This fever may be intermittent or
persistent.
Loss of Function and Mobility
As RA progresses, joint damage
can occur, leading to a loss of function and mobility. This can make it
difficult to perform daily activities, such as getting dressed, cooking, or
driving.
Associated Conditions
RA can also be associated with
other conditions, including:
§
Sjögren's Syndrome
Sjögren's syndrome is an
autoimmune disease that affects the exocrine glands, which produce tears and
saliva. When combined with RA, it is referred to as Sjögren's syndrome
secondary to rheumatoid arthritis.
Symptoms of Sjögren's syndrome
include:
·
Dry eyes: This can cause discomfort, burning,
and blurred vision.
·
Dry mouth: This can lead to difficulty
swallowing, speaking, and eating.
·
Fatigue
·
Joint pain and swelling
·
Dental problems
·
Vaginal dryness
§
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition
characterized by weakened bones, which can increase the risk of fractures.
People with RA are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis due to the
long-term use of certain medications and the impact of the disease on bone health.
Symptoms of osteoporosis may
include:
·
Back pain
·
Fractures (especially of the hip, wrist, or
spine)
·
Loss of height
·
Postural changes
If you are diagnosed with RA,
it is important to be aware of these associated conditions and to discuss them
with your healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment can help
manage these conditions and improve your overall quality of life.
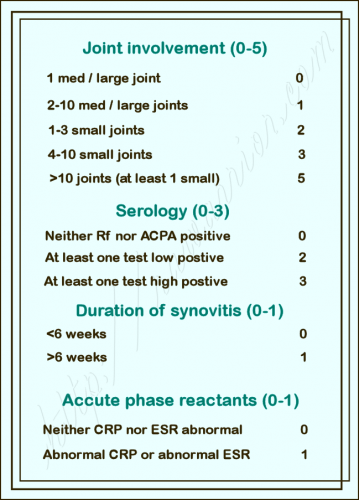
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) involves a
comprehensive evaluation to identify the characteristic signs and symptoms of
the disease. This process typically includes:
Medical History
A detailed medical history is
essential to understand the patient's symptoms, duration of illness, and any
family history of autoimmune diseases. The doctor will inquire about:
·
Joint pain and swelling
·
Morning stiffness
·
Fatigue
·
Weight loss
·
Fever
·
Any previous diagnoses or medical conditions
Physical Examination
A physical examination is
conducted to assess the joints for signs of inflammation, tenderness, and
swelling. The doctor may also evaluate the patient's range of motion and
overall physical function.
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests can help identify
markers of inflammation and autoimmune activity, which are common in RA. These
tests may include:
·
Rheumatoid factor (RF): A protein that is
often elevated in individuals with RA, but it may also be positive in other
conditions.
·
Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP)
antibodies: These antibodies are more specific to RA and are often positive
in individuals with the disease.
·
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and
C-reactive protein (CRP): These markers can indicate inflammation in the
body.
Imaging Studies
Imaging tests can help assess
joint damage and rule out other conditions. Common imaging studies used in the
diagnosis of RA include:
·
X-rays: Can show joint erosion and bone
damage that may occur in the later stages of RA.
·
MRI: Can provide more detailed images of
the joints and surrounding tissues, including soft tissue inflammation and
cartilage damage.
It is important to note that
no single test can definitively diagnose RA. A combination of these factors
is typically used to make a diagnosis. If RA is suspected, a rheumatologist, a
specialist in autoimmune diseases, can provide a definitive diagnosis and
recommend appropriate treatment.
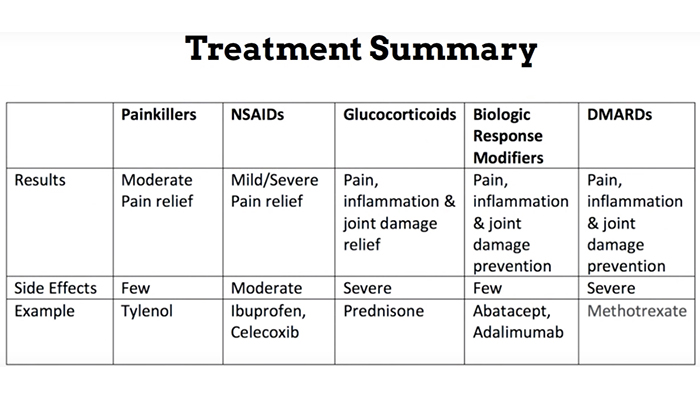
Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
The goal of RA treatment is to manage symptoms, reduce
inflammation, and prevent joint damage. A variety of treatment options may be
considered, tailored to the individual patient's needs and preferences.
Medications
·
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
(NSAIDs): NSAIDs help reduce pain and inflammation by blocking the
production of prostaglandins, substances that contribute to inflammation.
Common NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib.
·
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
(DMARDs): DMARDs are medications that can slow the progression of RA and
prevent joint damage. They work by suppressing the immune system. Common DMARDs
include methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine.
·
Biologics: Biologics are targeted
therapies that block specific parts of the immune system involved in RA. They
can be highly effective in managing RA symptoms, especially in patients who do
not respond well to other treatments. Examples of biologics include TNF inhibitors
(e.g., adalimumab, etanercept), interleukin-1 inhibitors (e.g., anakinra), and
interleukin-6 inhibitors (e.g., tocilizumab).
·
Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids are
powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can be used to treat flares of RA.
However, long-term use of corticosteroids can have side effects, so they are
typically used in short courses.
Lifestyle Modifications
·
Exercise and physical therapy: Regular
physical activity can help improve joint function, reduce pain, and maintain
strength. Physical therapists can provide tailored exercise programs to meet
the specific needs of individuals with RA.
·
Stress reduction techniques: Stress can
exacerbate RA symptoms. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing
can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
·
Dietary changes: While there is no
specific RA diet, some people may find that certain dietary changes can help
alleviate symptoms. Anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole
grains, and lean proteins, may be beneficial.
Alternative Therapies
·
Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves
inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and
improve overall well-being. Some studies suggest that acupuncture may be
helpful for managing RA symptoms.
·
Massage: Therapeutic massage can help
reduce muscle tension and improve circulation, which may provide relief from RA
pain.
Surgery
In severe cases of RA, joint
replacement surgery may be necessary to alleviate pain and improve function.
This involves replacing a damaged joint with an artificial joint.
It is important to work
closely with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate
treatment plan for you. The best approach may involve a combination of
these options, tailored to your individual needs and preferences.
Management and Lifestyle Changes
Living with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) requires a
multifaceted approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of
the disease. By incorporating medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and
emotional support, individuals can effectively manage RA symptoms and improve
their quality of life.
Image: Lifestyle Management in RA
Exercise and Physical Therapy
Regular physical activity plays a
crucial role in managing RA. Exercise can help:
·
Improve joint function: Gentle exercises
can strengthen muscles surrounding the joints, improving mobility and reducing
pain.
·
Reduce pain: Exercise can release
endorphins, the body's natural pain relievers.
·
Maintain strength: Regular physical
activity helps prevent muscle wasting, which can occur with RA.
Physical therapists can provide
personalized exercise programs tailored to individual needs and abilities.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress can exacerbate RA symptoms
and negatively impact overall well-being. It is important to implement stress
reduction techniques to manage stress levels effectively. Some helpful
techniques include:
·
Meditation: Meditation can help calm the
mind and reduce anxiety.
·
Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures,
breathing techniques, and meditation to promote relaxation and stress relief.
·
Deep breathing exercises: Deep breathing
can help slow down the heart rate, reduce anxiety, and improve focus.
Dietary Changes
While there is no specific RA
diet, some people may find that certain dietary changes can help alleviate
symptoms. Consuming a healthy diet rich in:
·
Fruits and vegetables: These are
excellent sources of antioxidants and vitamins, which can help reduce
inflammation.
·
Whole grains: Whole grains provide fiber
and complex carbohydrates, which can help regulate blood sugar levels.
·
Lean proteins: Lean proteins, such as
fish, chicken, and beans, are important for building and repairing tissues.
·
Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids,
found in fatty fish like salmon, can help reduce inflammation.
It is also important to limit or
avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and red meat, as these may contribute to
inflammation.
Sleep Management
Getting enough quality sleep is
essential for managing RA symptoms and overall health. Poor sleep can
exacerbate fatigue, pain, and stiffness. Establishing a regular sleep routine,
creating a relaxing sleep environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene can
help improve sleep quality.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily life,
you can effectively manage RA symptoms, improve your overall well-being, and
enhance your quality of life. It is important to work closely with your
healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan that best suits
your individual needs.
Complications and Prognosis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), if left untreated, can have
significant long-term consequences. These complications can significantly
impact a person's quality of life and may require ongoing management.
Joint Damage and Deformity
One of the most severe
complications of untreated RA is joint damage and deformity. As the disease
progresses, the inflammation can erode the cartilage and bone in the affected
joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. In severe cases, joint
deformity may occur, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
People with RA are at a higher
risk of developing cardiovascular disease, such as heart attack and stroke.
This increased risk is likely due to a combination of factors, including
inflammation, chronic stress, and the use of certain medications.
Osteoporosis and Bone Fractures
RA can also increase the risk of
osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones. This is partly due
to the long-term use of certain medications, such as corticosteroids, which can
reduce bone density. Osteoporosis can increase the risk of fractures,
especially in the hip, wrist, and spine.
Emotional and Mental Health Impact
Living with a chronic condition
like RA can have a significant emotional and mental health impact. Individuals
may experience feelings of frustration, sadness, anxiety, and depression. It is
important to seek support and counseling if you are struggling with the
emotional challenges associated with RA.
Prognosis
The prognosis for RA varies
depending on individual factors, such as the severity of the disease, the
timing of diagnosis, and the effectiveness of treatment. With early diagnosis
and appropriate management, many people with RA can live fulfilling lives.
However, it is important to be aware of the potential long-term consequences of
untreated RA and to work closely with your healthcare provider to manage the
condition effectively.
Current Research and Future Directions
Researchers are continually working to better understand the
disease and develop more effective treatments. Here are some of the current
areas of research:
1. Personalized Medicine
·
Genetic testing: Identifying genetic
markers associated with RA can help tailor treatment plans to individual
patients.
·
Biomarkers: Researchers are studying
biomarkers that can predict disease progression and response to treatment.
·
Precision medicine: This approach aims to
deliver the right treatment to the right patient at the right time.
2. Novel Therapeutics
·
Targeted therapies: Scientists are
developing drugs that specifically target the immune pathways involved in RA.
·
Combination therapies: Combining
different types of treatments may offer more effective outcomes.
·
Nanotechnology: Using nanotechnology to
deliver drugs directly to the affected joints can potentially reduce side
effects.
3. Lifestyle Interventions
·
Diet: Investigating the role of specific
dietary factors in RA, such as the Mediterranean diet or gluten-free diets.
·
Exercise: Exploring the optimal types and
intensity of exercise for individuals with RA.
·
Stress management: Developing effective
techniques to help patients manage stress and improve overall well-being.
4. Disease Progression and Prediction
·
Early diagnosis: Identifying early signs
and symptoms of RA to allow for timely intervention.
·
Predicting disease course: Developing
tools to predict how RA will progress in individual patients.
5. Improving Quality of Life
·
Fatigue management: Addressing the
debilitating fatigue associated with RA.
·
Mental health: Exploring the
psychological impact of RA and developing strategies to support patients'
emotional well-being.
·
Patient-reported outcomes: Using
patient-centered measures to assess the effectiveness of treatments and improve
quality of life.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex autoimmune disease that
can significantly impact a person's quality of life. While there is no cure,
effective management strategies can help individuals cope with the symptoms and
maintain a good quality of life. If you or someone you know is experiencing
symptoms of RA, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for
proper diagnosis and treatment.
Most Frequently asked Questions:
Can you recover from rheumatoid arthritis?
While there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), some
individuals may experience periods of remission where symptoms improve or
disappear. However, complete recovery is rare.
Can you live a long life with rheumatoid arthritis?
Yes, it is possible to live a long and fulfilling life with
RA. With proper management, including medication, therapy, and lifestyle
modifications, individuals can maintain a good quality of life.
What is the main cause of rheumatoid arthritis?
The exact cause of RA is unknown, but it is believed to be a
combination of genetic and environmental factors. The immune system mistakenly
attacks healthy tissues in the joints, leading to inflammation.
What is the best thing to do for rheumatoid arthritis?
The best approach for managing RA involves a multi-faceted
strategy, including:
- Medication:
To reduce inflammation and pain.
- Physical
therapy: To improve joint function and range of motion.
- Occupational
therapy: To help with daily activities and adapt to changes in
lifestyle.
- Lifestyle
modifications: Such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress
management.
What foods are bad for rheumatoid arthritis?
While more research is needed, some studies suggest that a
diet rich in red meat, processed foods, and sugary drinks may be associated
with increased inflammation.
Is rheumatoid arthritis curable?
Currently, there is no cure for RA. However, the goal of
treatment is to manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent joint
damage.
Is exercise good for rheumatoid arthritis?
Yes, exercise is generally beneficial for people with RA.
Low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and tai chi can help improve
joint function, reduce pain, and maintain overall health.
What is end stage rheumatoid arthritis?
End-stage RA is a severe condition where significant joint
damage has occurred, leading to limited mobility and disability. In some cases,
joint replacement surgery may be necessary.
Is rheumatoid arthritis a permanent condition?
Yes, RA is a chronic condition that typically lasts a
lifetime. However, with effective management, it is possible to maintain a good
quality of life.
Which drink is good for arthritis?
Water is essential for hydration and can help reduce joint
stiffness. Additionally, some studies suggest that green tea and turmeric may
have anti-inflammatory properties.
Which vitamin deficiency causes rheumatoid arthritis?
While vitamin deficiency is not the primary cause of RA,
some research suggests that low levels of vitamin D may be associated with an
increased risk of developing the condition.
Is RA caused by stress?
While stress may exacerbate RA symptoms, it is not the
direct cause of the disease. However, stress management techniques can help
improve overall well-being.
What is the best vitamin for rheumatoid arthritis?
Vitamin D is often recommended for people with RA, as it
plays a role in immune function and inflammation. However, it is important to
consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
What is the best exercise for arthritis?
Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and tai chi are
generally considered the best options for people with arthritis. It is
important to listen to your body and avoid activities that cause pain.
What is the most successful treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
The most successful treatment for RA often involves a
combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle modifications. The best
approach will vary depending on individual circumstances.
Which fruit is best for arthritis?
Fruits rich in antioxidants, such as berries and cherries,
may have anti-inflammatory properties and benefit people with arthritis.
Is milk bad for arthritis?
Some people with RA may find that dairy products exacerbate
their symptoms. However, this is not true for everyone. If you suspect that
dairy may be a trigger, consult with a healthcare provider.
Is egg bad for arthritis?
There is no definitive evidence that eggs are harmful for
people with arthritis. However, some individuals may find that certain foods,
including eggs, can trigger flare-ups.
Can I live a normal life with rheumatoid arthritis?
Yes, it is possible to live a normal life with RA. With
proper management, individuals can participate in many activities and enjoy a
good quality of life.
What is the permanent solution for rheumatoid arthritis?
Currently, there is no permanent cure for RA. However, the
goal of treatment is to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Is rheumatoid arthritis very serious?
RA can be a serious condition, especially if left untreated.
However, with effective management, it is possible to prevent severe
complications and maintain a good quality of life.
What is the best breakfast for arthritis?
A healthy breakfast that includes fruits, vegetables, and
whole grains can be beneficial for people with arthritis. Avoid processed foods
and sugary drinks.
How can I stop arthritis pain at night?
To help manage nighttime arthritis pain, consider using a
mattress that provides adequate support, taking pain medication as prescribed,
and using heat or cold therapy.
Is walking good for arthritis?
Walking is generally a good low-impact exercise for people
with arthritis. However, it is important to listen to your body and avoid
activities that cause pain.
Can rheumatoid arthritis go away?
While complete remission is rare, some people with RA may
experience periods of remission where symptoms improve or disappear.
How do I stop my RA from progressing?
Adhering to your treatment plan, maintaining a healthy
lifestyle, and managing stress can help prevent RA from progressing.
Is rheumatoid arthritis genetic?
Genetics play a role in the development of RA, but it is not
solely caused by genetic factors. Environmental factors may also contribute.
Which doctor is best for rheumatoid arthritis?
A rheumatologist is a specialist who treats conditions like
RA. They can diagnose the condition, prescribe appropriate medications, and
recommend other treatments.
How did I cured my RA naturally?
While there is no cure for RA, natural remedies like dietary
changes, exercise, and stress management can complement traditional medical
treatments and help improve symptoms.
What is the best treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
The best treatment for RA often involves a combination of
medication, therapy, and lifestyle modifications. The specific approach will
vary depending on individual circumstances.
Is rice good for arthritis?
Rice is generally considered a healthy food that can be
included in a balanced diet for people with arthritis. However, it is important
to avoid excessive consumption of refined carbohydrates.
Is sun good for arthritis?
Moderate sun exposure can help the body produce vitamin D.
However, excessive sun exposure can increase the risk of skin damage. It is
important to protect your skin from harmful UV rays.
Should I take B12 if I have rheumatoid arthritis?
While there is no specific evidence that B12 supplements are
particularly beneficial for RA, a deficiency of this vitamin can cause fatigue
and other symptoms. If you are concerned about a B12 deficiency, consult with a
healthcare provider.
What is the root cause of RA?
The exact root cause of RA is unknown, but it is believed to
be a combination of genetic and environmental factors that lead to an
autoimmune response.
Can RA occur suddenly?
While RA can sometimes develop gradually, it is also
possible for symptoms to appear suddenly.
Who is most at risk for rheumatoid arthritis?
Women are more likely to develop RA than men. The risk also
increases with age. Other factors that may increase the risk include family
history of autoimmune diseases and smoking.
Do bananas help with rheumatoid arthritis?
Bananas are a good source of potassium, which can help
regulate fluid balance in the body. However, there is no specific evidence that
they have any particular benefits for RA.
Does turmeric help RA?
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with
anti-inflammatory properties. Some studies suggest that turmeric supplements
may be beneficial for people with RA. However, more research is needed.
What foods are good for arthritis?
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean
proteins, and healthy fats can be beneficial for people with arthritis. Foods
with anti-inflammatory properties, such as fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and olive
oil, may also be helpful.
Which drink is good for arthritis?
Water is essential for hydration and can help reduce joint
stiffness. Additionally, some studies suggest that green tea and turmeric may
have anti-inflammatory properties.
Is walking good for RA?
Walking is generally a good low-impact exercise for people
with arthritis. However, it is important to listen to your body and avoid
activities that cause pain.
What is the fastest way to treat arthritis?
There is no quick fix for RA. Effective management requires
a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and self-care
strategies.
What foods are bad for rheumatoid arthritis?
While more research is needed, some studies suggest that a
diet rich in red meat, processed foods, and sugary drinks may be associated
with increased inflammation.
Which is the best treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
The best treatment for RA often involves a combination of
medication, therapy, and lifestyle modifications. The specific approach will
vary depending on individual circumstances.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rheumatoid-arthritis-causes-5b0d72f93037130037061a4c.png)
Comments
Post a Comment